All cases are discussed by: Dr. Dolphine Oda, UW-Oral Pathology Biopsy Service
October 2019: Triangular radiolucent lesion between teeth #s 5 & 6
Contributed by:
Dr. Todd Carter
Maui OMS, Maui, Hawaii
Case Summary and Diagnostic Information
This is a 27-year-old female who had an incidental bony lesion between teeth #s 5 & 6. This lesion was asymptomatic and did not cause expansion in the area.
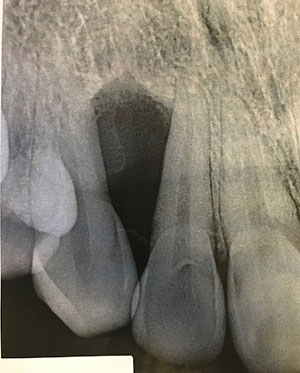
This is a 27-year-old female who had an incidental bony lesion between teeth #s 5 & 6. This lesion was asymptomatic and did not cause expansion in the area. This lesion was first noticed by her general dentist and was referred to an oral surgeon. The bone supporting the two teeth was compromised, but the teeth were not mobile. The lesion is radiolucent and is triangular in shape
(Figure 1). It may be causing mild displacement of the roots of teeth #s 5 & 6, but it is not significant. The area was described as a solid mass with a gelatinous consistency. It was about 8mm in size. The lesion did not perforate into the maxillary sinus or the nasal cavity.

Figure 1 This is a periapical lesion taken at presentation. It shows a well-demarcated radiolucency triangular in shape between teeth #s 5 & 6. The teeth are mildly divergent.
The patient’s past medical history is significant for asthmas and anxiety.
The primary periapical radiograph (Figure 1) demonstrated a well-demarcated radiolucency between teeth #s 5 & 6. This lesion caused very mild divergence of the two teeth but no clinical expansion was noted. Both teeth are vital and show no evidence of pathology.
Histologic examination revealed multiple small pieces of soft tissue madeup of connective tissue stroma with odontogenic epithelial islands (Figure 2-4). The connective tissue cellular with spindle-shaped fibroblasts suspended on delicate collagen fibers. The epithelial islands comprise a significant portion of the specimen and are madeup of variable shapes and sizes. They have flat epithelial cells at the periphery and the center of these islands contains squamous epithelial cells (Figure 3). Some of the epithelial islands showed central degeneration of the cells and few apoptotic cells (Figure 4).
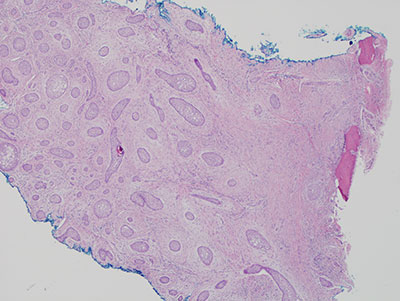
Figure 2 Low power (x40) H & E stained section shows a mass of cellular connective tissue stroma surrounding many epithelial islands of variable shapes and sizes.
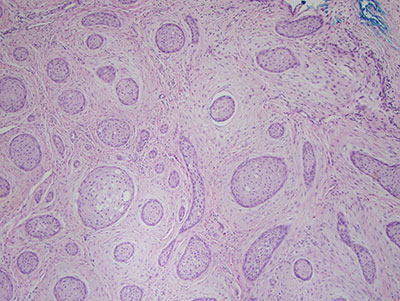
Figure 3 Higher power (x100) H & E stained section with closer look at the periphery of the epithelial islands. The cells at the periphery are flat. The center of the islands is filled with squamous well-differentiated epithelial cells.
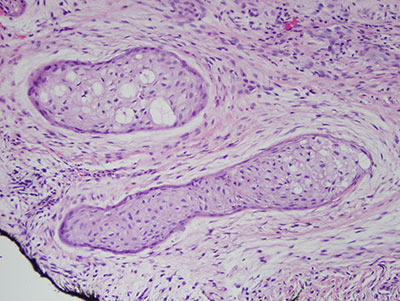
Figure 4 Higher power (x200) H & E stained section with closer look at the center of the epithelial islands where few degenerating epithelial cells and apoptotic cells are identified.
After you have finished reviewing the available diagnostic information