All cases are discussed by: Dr. Dolphine Oda, UW-Oral Pathology Biopsy Service
Large well-demarcated swelling on the upper lip
Contributed by: Dr. David Haralson
Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, Seattle, WA
Case Summary and Diagnostic Information
This is a 21-year-old male who presented with a large smooth-surfaced, pink, firm and movable nodule on the upper lip.
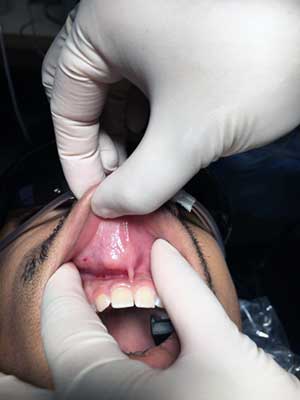
This is a 21-year-old male who presented with a large smooth-surfaced, pink, firm and movable nodule on the upper lip (Figure 1). It was around 2 cm in diameter at its greatest dimension and was slowly increasing in size over the last six months. It is otherwise asymptomatic. The overlying mucosa is pink and shows no evidence of ulceration.

Figure 1 This photograph is taken at first clinical presentation and demonstrates a well-demarcated, large submucosal nodule in the upper lip. It has a smooth surface, same color as the surrounding mucosa.
The patient’s past medical history is negative for smoking, allergies or any systemic illness.
The patient reported a slowly enlarging lesion in the upper lip over the last six months duration. The swelling was not painful and was pink, firm and movable. It was around 2 cm in diameter.
Under IV general anesthesia, 1 x 2cm horizontal elliptical incision outlined over upper lip mass was performed. Incision carried through mucosa with bovie electrocautery. The lesion was identified and dissected through the submucosa and orbicularis muscle (Figure 2). It was removed in whole (Figure 3). The site was irrigated; the deep muscle layer and mucosa were sutured with 3-0 vicryl sutures.
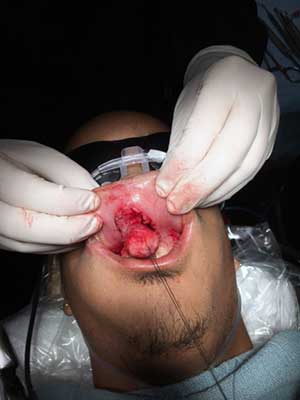
Figure 2 This photograph is taken at surgery, note the large encapsulated nodule being peeled from the inner mucosa of the upper lip.
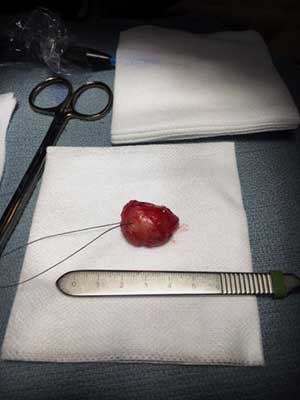
Figure 3 This photograph is taken at surgery demonstrating the gross morphology of the encapsulated nodule which is a little over 2 cm in greatest dimension.
Histologic examination reveals two representative large sections from a large and multisected piece of soft tissue composed of a neoplasm partially surrounded by a thin capsule (Figures 4-5). This neoplasm is made up of duct-like structures as well as sheets and clusters of myoepithelial cells suspended on collagen fibers (Figures 4-6). The connective tissue background is loose and myxoid in some areas and fibrotic in others (Figures 5-6). Some of the duct-like structures are highly dilated while others are of variable shapes and sizes and contain mucoid coagulant.
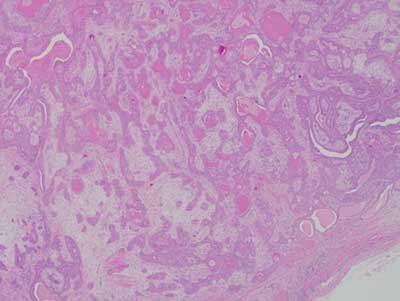
Figure 4 Low power (x40) the H & E histology reveals an encapsulated neoplasm made up of duct-like structures and sheets of myoepithelial cells suspended on mixed collagenous and focally myxoid matrix.
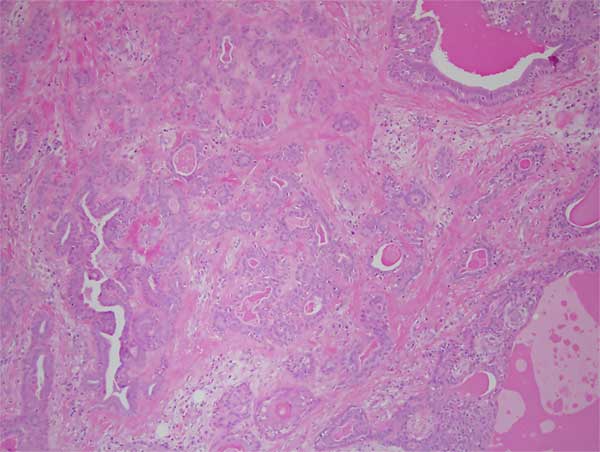
Figure 5 Low power (x100) the H & E histology with a closer look at the neoplasm with duct-like structures and myoepithelial cells.
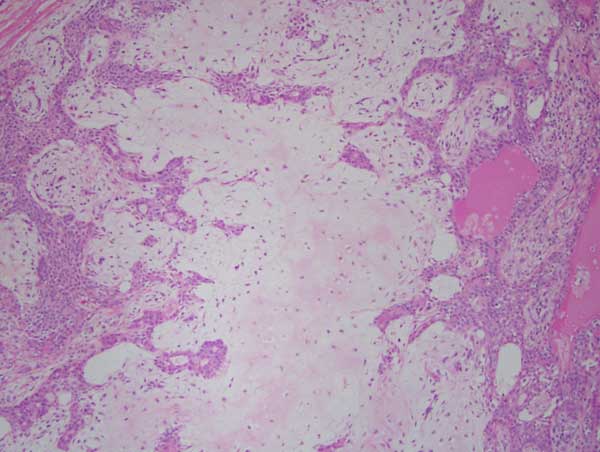
Figure 6 High power (x200) the H & E histology with a closer look at the sheets of the myoepithelial cells and the chondromyxoid stroma.
After you have finished reviewing the available diagnostic information