Return to Case of the Month Archives
May 2009: Multiple small nodule; lips and bilateral buccal mucosa
Dolphine Oda, BDS, MSc
doda@u.washington.edu
Contributed by
Drs. Abraham Estes and John Evans
Department of Oral Surgery, University of Washington, WA
Bellevue, WA
Case Summary and Diagnostic Information
This is an 8-year-old Hispanic male who was seen at the University of Washington Oral Surgery Clinic. He presented with a chief complaint of multiple small nodules on the upper and lower lips, bilateral buccal mucosa and tongue.
Diagnostic Information Available
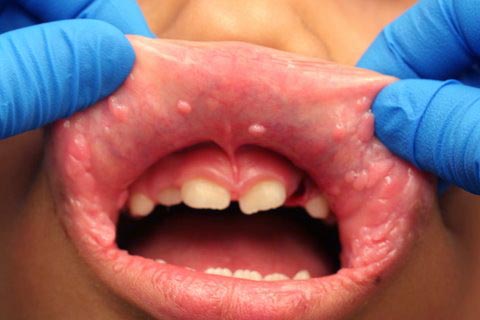
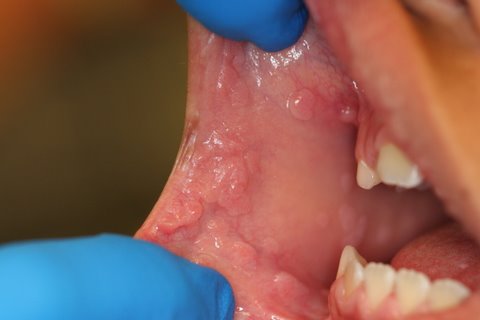
This is an 8-year-old Hispanic male who was seen at the University of Washington Oral Surgery Clinic. He presented with a chief complaint of multiple small nodules on the upper and lower lips, bilateral buccal mucosa and tongue. They were of unknown duration and were otherwise asymptomatic (Figures 1 & 2). There were no such lesions on the skin or on the fingers. There was no family history of such lesions. The nodules ranged from 2 to 5 mm in size and had intact surfaces. They were the same color as the surrounding mucosa.
Figure 1 Photograph taken at first clinical presentation to University of Washington Oral Surgery Clinic. Note the multiple, small, pink, sessile and exophytic nodules on the upper lip and bilateral commissures. They were also present on the lower lip.
Figure 2 Photograph taken at first clinical presentation to University of Washington Oral Surgery Clinic. Note the coalescing multiple, small, pink, sessile and exophytic nodules on the right buccal mucosa. They were present on the left buccal mucosa as well.
The patient’s past medical history is not significant for any disease and his family history is negative for such lesions.
The patient’s parents are not sure when they appeared but state that they have been present for more than three years. They are multiple nodules, the same color as the surrounding mucosa and are present on the upper and lower labial mucosa and bilateral buccal mucosa, more so anterior buccal mucosa, near the commissures. They are reportedly “itchy” and have some “burning sensation”. There is no family history of such lesions.
Figure 1 Photograph taken at first clinical presentation to University of Washington Oral Surgery Clinic. Note the multiple, small, pink, sessile and exophytic nodules on the upper lip and bilateral commissures. They were also present on the lower lip.
Figure 2 Photograph taken at first clinical presentation to University of Washington Oral Surgery Clinic. Note the coalescing multiple, small, pink, sessile and exophytic nodules on the right buccal mucosa. They were present on the left buccal mucosa as well.
Treatment
Under local anesthesia one of the 0.5 cm nodules from the left buccal mucosa was biopsied and sent for histologic evaluation.
Incisional Biopsy
Histologic examination of the H & E section revealed a thick surface epithelium with mild and broad papillary configuration supported by connective tissue. The surface epithelium was covered by a thin layer of parakeratin and the spinous layer was thick in most parts (Figure 3). Multiple mitosoid cells were identified within the middle and deep spinous layer (Figure 4). Also present were epithelial cells with pyknotic nuclei and empty-looking cytoplasm consistent with koilocytes.
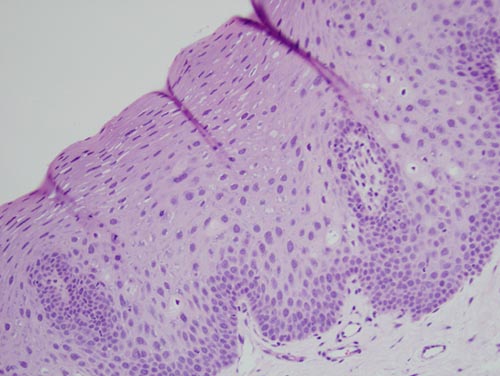
Figure 3 Low power (x100) H & E histology shows oral mucosa covered by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with mitosoid cells, koilocytes and a thick spinous layer. The underlying connective tissue is loose and vascula.
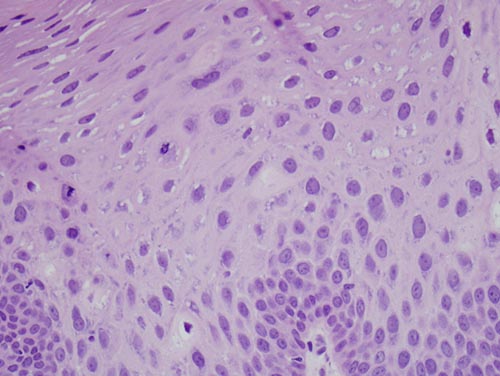
Figure 4 High power (x200) higher power H & E histology taking a closer look at the multiple mitosoid cells within the mid to high spinous layer.
After you have finished reviewing the available diagnostic information