Program Description
The Oral Health Sciences PhD program usually requires five years. Students are expected to devote the full twelve-month year to their graduate work (allowing time for vacation and holidays). Graduate students will have the opportunity to assist in the teaching program of the department as a practical means of gaining experience in the presentation of lectures and laboratory work. Some opportunities exist to teach to dental and graduate students.
Courses Requirements
The course requirement is a minimum of 90 credits (including at least 27 credits of thesis). Through their coursework, students are expected to gain proficiency in one or more basic biologic sciences and to master modern biological approaches in addition to gaining expertise in the subject area of oral and craniofacial sciences. At least 19 credit hours must come from courses in departments other than Oral Health Sciences, and of the 19, 12 must be science courses. Of the 19 credits, a minimum of six (6) credits must be CONJ or PABIO courses, a minimum of six (6) credits must be non-OHS science courses, plus at least one non-science course should be completed. These will include courses offered through the Molecular and Cell Biology Program and courses selected to match the basic science interests of the student. Cross-disciplinary training in Bioengineering is also available. Courses in the School of Public Health such as the Epidemiology series are also available to students interested in Dental Public Health research. All graduate students are also expected to attend and participate in departmental seminars (OHS 575).
Following is an approximate timeline for completion of the PhD degree. Because each student’s program and research goals will vary, completion of the requirements for the PhD degree may not necessarily follow this timeline.
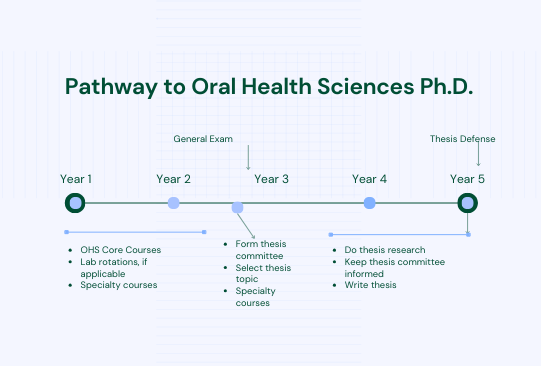
Pathway to Oral Health Sciences PhD (PDF)
Schedule by Year
Initial Course Work. All new students meet with the Graduate Program Coordinator before the start of classes in the Summer or Autumn Quarter to consider the student’s course work. The selection of courses will depend on the student’s background, research goals, and interests.
Research Rotation. During each quarter of the first year of graduate study, the student will register for OHS 578, Research Techniques. The purpose of this course is for students to carry out research projects with 1-2 faculty members in order to prepare for the choice of their PhD project mentor and to learn a variety of research methods.
Course Work. Students will continue to take courses that will include the remainder of the core courses required in Oral Health Sciences and courses in other disciplines relevant to the student’s dissertation research.
Teaching. Students are encouraged to take elective courses offered through the Medical Education and Graduate School which will help them in their future teaching careers. Also, beginning in the second year, graduate students will have the opportunity to take part in teaching one of the Department courses for undergraduate dental students. This experience prepares students for teaching responsibilities after receipt of the PhD and provides a good opportunity for consolidation of the student’s general oral biology background.
Research. Early in the second year of study, the student is expected to choose a thesis adviser and to define a dissertation problem.
The Supervisory Committee. Once a thesis mentor and research direction have been chosen, the student and mentor will select a Supervisory Committee. This should be done in year two of the training. The committee is composed of at least four faculty members, at least three of whom (Including the Chair and the Graduate School Representative) must be members of the Graduate Faculty with an endorsement to chair doctoral committees. The Graduate Program Coordinator will forward the list of recommended committee members to the Dean of the Graduate School who will officially appoint the Supervisory Committee. In accordance with Graduate School regulations, the Supervisory Committee will be responsible for advising and directing the student throughout the PhD program.
The General Examination. Late in the second year, the student will take the General Examination. This examination is in the format of a written research grant proposal that is presented to the PhD supervisory committee. All required coursework must be completed at this time. The purposes of this examination are (1) to determine whether the student is capable of recognizing an important research question in oral and craniofacial sciences, (2) to determine whether the student is able to develop this question into a comprehensive proposal complete with preliminary findings and suggested methods of procedure, and to orally defend the proposal, and (3) to provide the student an opportunity to receive feedback from the Supervisory Committee on the proposed research project.
The student will primarily engage in thesis research and additional advanced coursework.
The Dissertation and the Dissertation Examination. When the candidate has completed the research project, written the dissertation, and had it approved by the reading committee, the mentor will obtain approval from the Graduate School and set a date for the Final Examination. The Final Examination will be concerned principally with the subject matter of the dissertation and is conducted as an open seminar followed by examination by the Supervisory Committee.
The research project for the PhD dissertation will be chosen by the candidate and adviser and be approved by the candidate’s Supervisory Committee. The research must represent a worthy and fundamental contribution showing originality in concept and implementation.
Courses
The following courses are mandatory program requirements:
| Course No. | Course Title | Credits Hrs. | Quarter Offered |
|---|---|---|---|
| OHS 501 | Critical Thinking in OHS: Craniofacial Biology and Oral Health Span | 2 | A |
| OHS 502 | Critical Thinking in OHS: Oral Microbiome | 2 | W |
| OHS 503 | Critical Thinking in OHS: Clinical Dental Research | 2 | Sp |
| OHS 568 | Biostatistics in Dentistry | 3 | S |
| OHS 575 | Oral Health Sciences Seminars | 1 | A, W, Sp |
| OHS 578 | Research Techniques in Oral Health Sciences (lab rotations- minimum of 2 required) |
2 | A, W, Sp, S |
| OHS 579 | Molecular Biology | 2 | S |
| OHS 600 | Independent Study/Research | var | A, W, Sp, S, |
| OHS 800 | Doctoral Dissertation (a minimum of 27 credits needed) |
var | A, W, Sp, S |
Following is an example list of the CONJ/PABIO courses.
| Course No. | Course Title | Credit Hrs. | Quarter Offered |
|---|---|---|---|
| CONJ 504 | Molecular Medicine | 1.5 | Sp |
| CONJ 524 | Structural Basis of Signal Transduction | 1.5 | W |
| CONJ 526 | Introduction to Systems Biology | 1.5 | W |
| CONJ 530 | Directing Stem Cells Toward Regenerative Med | 3 | W |
| CONJ 531 | Signaling Mechanisms in Excitable Cells | 1.5 | A |
| CONJ 532 | Signal Transduction | 2 | A |
| CONJ 533 | Dynamic Chromosome | 1.5 | A |
| CONJ 534 | Problems in Nervous System Development | 1.5 | W |
| CONJ 537 | Mechanism of Transcriptional Regulations | 1.5 | A |
| CONJ 539 | Biological Basis of Neoplasia | 1.5 | Sp |
| CONJ 541 | Molecular Biology of Cellular Processes | 1.5 | Sp |
| CONJ 542 | Cell Biology of Development | 3 | W |
| CONJ 544 | Protein Structure, Modification and Regulation | 1.5 | W |
| CONJ 545 | Molecular Interactions and Medicine | 1.5 | Sp |
| CONJ 546 | Survey of Technologies for Molecular Biology | 1.5 | A |
| CONJ 548 | Modeling Proteins and Proteomes | 1.5 | W |
| CONJ 549 | Microbial Population Biology | 1.5 | W |
| CONJ 550 | Clinical Infectious Diseases | 3 | W |
| CONJ 551 | Immunity | 1.5 | Sp |
| CONJ 552 | Metabolic Flexibility in Biology | 1.5 | A |
| CONJ 557 | Microbial Evolution | 2 | Sp |
| CONJ 558 | Prokaryotic Biology | 1.5 | W |
| CONJ 583 | Molecular Targets in Cancer | 1.5 | A |
| PABIO 536 | Bioinformatics and Gene Sequence Analysis | 3 | Sp |
Some students may need to take some lower level division courses in order to prepare for required classes. See the following list for suggestions:
| Course No. | Course Title | Credit Hrs. | Quarter Offered |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIOC 405 | Introduction to Biochemistry | 3 | A |
| BIOC 406 | Introduction to Biochemistry | 3 | W |
| BIOL 411 | Developmental Biology | 4 | A, W |
| MICROM 411 | Bacterial Genetics | 5 | W |
| IMMUN/MICRO 441 | Introduction to Immunology | 4 | A |
Following is an example list of non-OHS science electives. Students are expected to take include courses in bioengineering, epidemiology, immunology, or other basic biological/medical sciences as appropriate for their research interests. The student will work with the Graduate Program Director and their mentor to select appropriate elective courses in their chosen basic biological science pathway. The list below is not meant to be exhaustive. Consult with the Graduate Program Director for potential approval of substitutions.
| Course No. | Course Title | Credit Hrs. | Quarter Offered |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIOC 530 | Introduction to Structural Biology | 3 | A |
| BIOEN 501 | Molecular Bioengineering | 4 | varies |
| BIOEN 502 | Cellular Bioengineering | 4 | varies |
| OHS 571 | Clinical Epidemiology | 2 | S |
| GENOME 551 | Gene Regulation | 1.5 | varies |
| GENOME 552 | Genome Analysis | 1.5 | A |
| GENOME 553 | Advanced Genome Analysis | 1.5 | varies |
| IMMUN 532 | Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Disease | 4 | W |
| MCB 532 | Human Pathogenic Viruses | 3 | A |
| MICROM/IMMUN 441 | Intro to Immunology | 4 | A |
| MICROM 445 | Medical Virology | 2 | Sp |
| MICROM 553 | Interactions of Bacteria with Their Hosts | 3 | Sp, odd years |
| NEUSCI 401 | Neuroscience | 3 | Sp |
| NEUSCI 402 | Diseases of the Nervous System | 3 | W |
| NEUSCI 403 | Computational Models for Cognitive Neuroscience | 3 | W |
| NEUSCI 404 | Neuropharmacology | 3 | Sp |
| PABIO 551 | Biochemistry & Genetics of Proteins & Hosts | 4 | A |
| PABIO 552 | Cell Biology of Human Pathogens & Disease | 4 | W |
| PABIO 553 | Survival Skills for Scientific Research | 2 | W |
| PABIO 568 | Molecular Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases | 2 | W |
| ORTHO 580 | Cranial Anatomy | 2 | S |
| Course No. | Course Title | Credit Hrs. | Quarter Offered |
|---|---|---|---|
| DENTPC 564, 565 (Yr 1 = 564; Yr 2 = 565) |
Clinical & Histopathological Correlation | 2 | A, W, Sp, S |
| DENTPC 574 | Oral Pathology | 3 | Sp |
To prepare for teaching, students may take at least one class on educational methods. In addition, students may train undergraduate students enrolled in OHS 449 (Undergraduate Research). Consult with your PI. Such credits will not fulfill the requirement for non-OHS science courses but will count toward the total credits required. Suggested courses include, but are not limited to:
| Course No. | Course Title | Credit Hrs. | Quarter Offered |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIME 520 | Teaching Methods in Medical Education | 2 | varies |
| BIME 521 | Evaluation of Learning in the Health Sciences | 3 | varies |
| OHS 562 | Supervised Teaching in Oral Health Sciences | Var. | A, W, Sp, S |
Students are also required to attend and participate in the Biomedical Research Integrity Series. This is a non-credit summer course taught through the Department of Bioethics and Humanities and consists of a series of lectures and discussion groups. Each student will need to attend a minimum of three lectures and three discussion groups. NIH Trainees are required to attend every year of the duration of their federal funding.